Download Champions' latest SITC 2019 Poster
Development of a Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) ImmunoGraft Platform to Evaluate the Pharmacodynamics of Immuno-Oncology (IO) Therapeutics
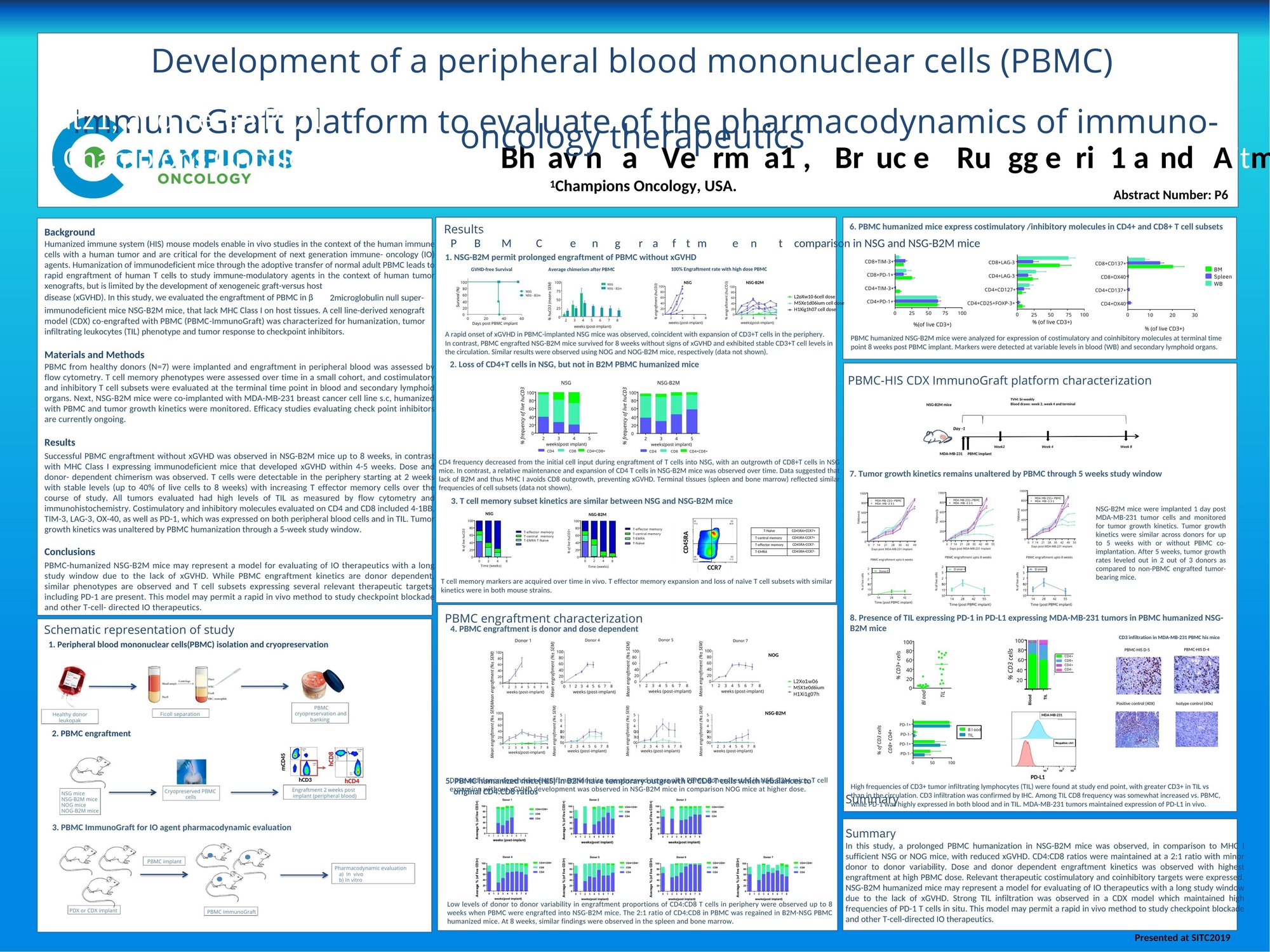
Humanized immune system (HIS) mouse models, which incorporate human immune cells and tumors, are crucial for developing next-generation immune-oncology agents. The adoptive transfer of human PBMCs into immunodeficient mice allows the study of immune-modulatory agents in human tumor xenografts but is often limited by the development of xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease (xGVHD). This study evaluated the use of β2-microglobulin null immunodeficient mice (NSG-B2M) that lack MHC Class I on host tissues, preventing xGVHD. The mice were co-engrafted with PBMCs and a breast cancer cell line to assess immune system humanization, tumor-infiltrating leukocyte (TIL) phenotype, and tumor response to checkpoint inhibitors. Successful PBMC engraftment without xGVHD was observed in NSG-B2M mice, providing a stable platform for immune-oncology studies.
- Humanized immune system (HIS) mouse models, using PBMCs and human tumors, are essential for studying immune-oncology agents.
- NSG-B2M mice, which lack MHC Class I, enable successful PBMC engraftment without xGVHD, providing a stable model for in vivo immune-oncology research.
- This model shows stable T-cell engraftment and expression of relevant immune markers like PD-1, making it suitable for evaluating checkpoint inhibitors and other T-cell directed therapies.